First Aid for Hypertension: Quick Responses for High Blood Pressure
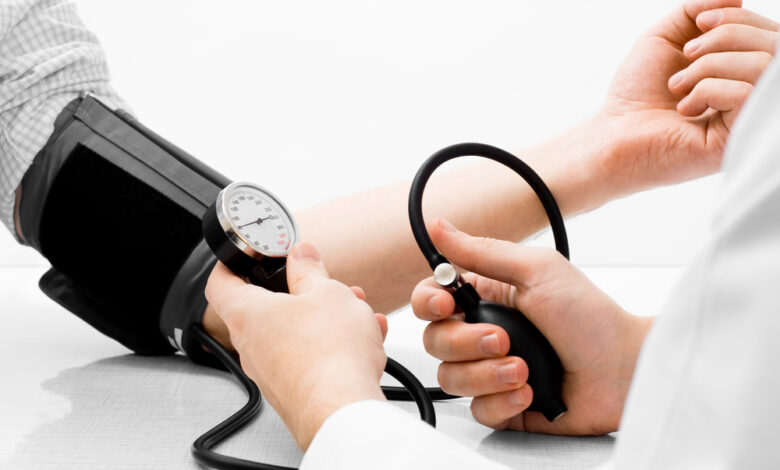

Understanding Hypertension
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common health condition that, if left unmanaged, can lead to serious complications such as heart disease and stroke. Understanding the basics of first aid for hypertension is crucial for providing immediate support when needed.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of hypertension is the first step in offering assistance. Symptoms may include severe headaches, vision problems, chest pain, difficulty breathing, and an irregular heartbeat. In emergency situations, it’s vital to be aware of these signs and respond promptly.
Urgent Response Measures
If someone is experiencing a hypertensive crisis, characterized by a sudden and severe increase in blood pressure, it requires urgent attention. Follow these quick response measures:
1. Call Emergency Services:
The first action is to call emergency services. High blood pressure emergencies can lead to serious health risks, and professional medical assistance is crucial.
2. Keep the Person Calm:
Anxiety and stress can exacerbate high blood pressure. Encourage the person to sit down, relax, and try to remain calm while waiting for medical help.
3. Check Medication:
If the person has prescribed medication for hypertension, check if they have taken it recently. If the medication is available, assist them in taking it as prescribed.
4. Monitor Vital Signs:
Keep an eye on vital signs such as heart rate and breathing. If the person’s condition worsens, be prepared to perform CPR if necessary.
Non-Emergency Measures
For individuals with a history of hypertension or moderately elevated blood pressure, there are non-emergency measures that can help manage the condition:
1. Encourage Rest:
In non-emergency situations, encourage the person to rest and take it easy. Avoiding physical exertion can help lower blood pressure.
2. Hydrate:
Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and can contribute to maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. Encourage the person to drink water regularly.
3. Modify Diet:
A heart-healthy diet low in sodium and rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can contribute to blood pressure management. Offer guidance on making healthier food choices.
4. Encourage Regular Monitoring:
For individuals with hypertension, regular blood pressure monitoring is crucial. Encourage them to check their blood pressure regularly and report any significant changes to their healthcare provider.
Lifestyle Recommendations
In addition to immediate first aid measures, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing hypertension:
1. Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking or swimming, can contribute to better blood pressure control.
2. Healthy Diet:
Adopting a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while reducing sodium intake supports overall cardiovascular health.
3. Stress Management:
Encourage stress-reducing activities such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga to promote emotional well-being.
4. Limit Alcohol and Tobacco:
Limiting alcohol intake and quitting smoking are essential steps in managing hypertension and improving overall health.
In conclusion, first aid for hypertension involves a combination of immediate response measures and long-term lifestyle modifications. By recognizing symptoms, responding promptly in emergencies, and promoting healthy habits, we can contribute to better blood pressure control and overall cardiovascular well-being. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment.